SIPO ( Serial Input Paralel Output ) Register ini merupakan kebalikan dari register PISO, jika seperti yang terlihat pada gambar berikut. Gambar 5.5 SIPO ( Serial Input Paralel Output ) Dalam tipe ini, data disajikan satu bit pada satu saat lalu digeser masuk pada setiap pulsa clock.
A serial-in, parallel-out shift register is similar to the in that it shifts data into internal storage elements and shifts data out at the serial-out, data-out, pin. It is different in that it makes all the internal stages available as outputs.
Therefore, a serial-in, parallel-out shift register converts data from serial format to parallel format. An Example of Using Serial-in, Parallel-out Shift Register If four data bits are shifted in by four clock pulses via a single wire at data-in, below, the data becomes available simultaneously on the four Outputs Q A to Q D after the fourth clock pulse. The practical application of the serial-in, parallel-out shift register is to convert data from serial format on a single wire to parallel format on multiple wires. Let’sl illuminate four LEDs (light emitting diodes) with the four outputs ( Q A Q B Q C Q D).
The above details of the serial-in, parallel-out shift register are fairly simple. It looks like a serial-in, serial-out shift register with taps added to each stage output. Serial data shifts in at SI (Serial Input). After a number of clocks equal to the number of stages, the first data bit in appears at SO (Q D) in the above figure. In general, there is no SO pin. The last stage (Q D above) serves as SO and is cascaded to the next package if it exists.
Serial-in, Parallel-out vs. Serial-in, Serial-out Shift Register If a serial-in, parallel-out shift register is so similar to a serial-in, serial-out shift register, why do manufacturers bother to offer both types?
Windows xp sp3 2010 all oem original iso download free. The steps to install windows XP are simple and easy. Follow this tutorial which tells How to install Windows XP (SP3) via USB Drive. Save it on your PC.
Why not just offer the serial-in, parallel-out shift register? The answer is that they actually only offer the serial-in, parallel-out shift register, as long as it has no more than 8-bits. Note that serial-in, serial-out shift registers come in bigger than 8-bit lengths of 18 to 64-bits. It is not practical to offer a 64-bit serial-in, parallel-out shift register requiring that many output pins. See waveforms below for above shift register. The shift register has been cleared prior to any data by CLR’, an active low signal, which clears all type D Flip-Flops within the shift register. Note the serial data 1011 pattern presented at the SI input.
This data is synchronized with the clock CLK. This would be the case if it is being shifted in from something like another shift register, for example, a parallel-in, serial-out shift register (not shown here). On the first clock at t1, the data 1 at SI is shifted from D to Q of the first shift register stage. After t2 this first data bit is at Q B. After t3 it is at Q C.
After t4 it is at Q D. Four clock pulses have shifted the first data bit all the way to the last stage Q D. The second data bit a 0 is at Q C after the 4th clock. The third data bit a 1 is at Q B. The fourth data bit another 1 is at Q A.
Thus, the serial data input pattern 1011 is contained in ( Q D Q C Q B Q A). It is now available on the four outputs. It will available on the four outputs from just after clock t 4 to just before t 5.
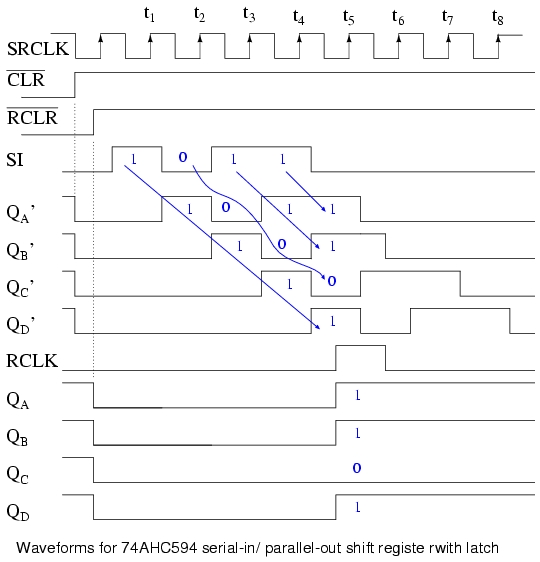
This parallel data must be used or stored between these two times, or it will be lost due to shifting out the Q D stage on following clocks t 5 to t 8 as shown above. Serial-in, Parallel-out Devices Let’s take a closer look at serial-in, parallel-out shift registers available as integrated circuits, courtesy of Texas Instruments.
Most Popular Articles
- Ayrton Senna Principles Of Race Driving Pdf Merge
- Vray Crack For Sketchup Mac Os
- Vampire Weekend Contra Album Rar Google
- Codegear Rad Studio 2007 Serial Number
- Servidores Linux Guia Prtico Carlos E Morimoto Download Pdf
- Descargar Mp3 De 01 El Polaco Enterrarlos Dj Eric 4 Mp4 Download
- Contoh Kertas Cadangan Program Khidmat Masyarakat
- Advanced Ace Hack Kit Htc Desire Hd Backup Cameras
- Harley Transmission Serial Numbers
- How To Install Gm Mdi Manager Etas
- Autocad 2004 Torrent Download With Crack
- Windows Xp Sp2 Dengan Serial Number
- Driver Xerox Docuprint P1202 Windows 7